Gap Between Cpt and Opt and Continue Employment
International students often look for work options right after their Masters in the USA. Yet, many employment opportunities are strongly restricted and have many complex rules. So, here's everything you need to know about options like CPT, OPT, and most importantly, the difference between CPT vs OPT.
Table of Contents
- What is CPT?
- CPT Types
- CPT Eligibility
- How to apply for CPT
- What is OPT?
- OPT Types
- OPT Eligibility
- STEM OPT Extension Eligibility
- How to apply for OPT
- What's next?
- FAQs
If you are an F-1 international student, you will have the option of training in the United States. But which is the best option for training? What are the rules of employment? That is where work options such as CPT vs. OPT come in.
While OPT and CPT have many similarities, there are actually very distinct differences when it comes to the application process. You can participate in practical training during your program or after the course. International students are eligible to seek employment under special circumstances and cannot do so without prior work authorization.
There are two types of practical training available: Curricular Practical Training (CPT) and Optional Practical Training (OPT). Continue to read about the Curricular Practical Training &Optional Practical Training qualifications you may need as an F-1 international student.
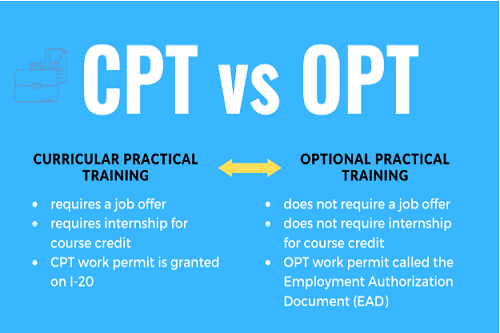
What is CPT?
Curricular Practical Training (CPT) is temporary employment authorization for F-1 international students. CPT allows students to train or receive an internship related to their major field of study. It also allows them to be off-campus and gain amazing experiences. CPT internships must meet the following conditions: a degree requirement or a course requirement.
Many majors require the completion of an internship or work experience, aka CPT, in order for you to graduate and complete your degree. As for the course requirement, you may be enrolled in an internship or work experience in order to receive a grade.
CPT Types
Curricular Practical Training includes either part-time or full-time training. If you are approved for part-time CPT, you are allowed to work up to 20 hours or less within a week. If approved for full-time CPT, you will be allowed to work more than 20 hours per week.
As a student, if you assemble 12 months of full-time CPT, you will not be eligible for OPT. You need to keep this in mind while considering CPT vs. OPT. Also, remember that independent studies will not be accepted by CPT.
CPT Eligibility
Students may apply for CPT when they are currently F-1 international students. You must also have been enrolled full-time for at least one academic year prior to your suggested CPT start date. Students must have a declared major and be enrolled full-time in order to receive their preferred internship. You are required to enroll in an internship or course that is designed for practical learning. CPT will require a letter of agreement from an employer.
How to apply for CPT
In order to apply for CPT, make sure to confirm your eligibility and the requirements. Students must contact their academic advisor and get informed about the internship course credit policy in their specific academic department. You must also find an internship or have a job offer. Be sure to complete the adviser and student section of the application and submit! You must allow 3 weeks for your application to process, so be patient.
What is OPT?
Optional Practical Training (OPT) is an opportunity given to F-1 international students that continue to maintain their status, and if eligible, they may apply for 12 months of OPT. OPT provides hands-on work experience related to your chosen major.
You may also work under OPT after you have completed your program. If you are approved, you will receive an Employment Authorization Document (EAD). An EAD card is what allows you to work fully authorized in the United States.

Approved students are required to report all information to the Student and Exchange Visitor Program. You may apply for 12 months of OPT at each level of education.
OPT Types
There are three types of Optional Practical Training (OPT): Pre-completion OPT, Post-completion OPT, and STEM OPT extension. Pre-completion OPT means the period before your program's end date. That period will be deducted from your 12 months of OPT eligibility. Most students prefer post-completion OPT, which begins after you complete your degree. A STEM OPT 24-month extension allows some STEM majors to extend their post-completion OPT.
OPT Eligibility
Students are eligible for OPT if they currently maintain F-1 international student status. You must also have been enrolled for full-time study for at least one academic school year. OPT eligibility requires you to physically attend classes in person in the United States at the time that you apply.
As mentioned, you will be denied eligibility if you have completed more than 12 months of CPT. Students who are eligible for OPT are not required to have a job offer or a Social Security number. OPT has a filing fee of $410 required by the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services.
STEM OPT Extension Eligibility
In order to qualify for the 24-month STEM OPT extension, you must have F-1 international student status. Students must also be working in a period post-completion of their OPT. To be eligible, you must have a bachelor's or a higher degree in an eligible STEM field. You must also currently be participating in a regular period of OPT.
The extension will start exactly after the last day of your regular OPT. You must also have a paid job offer that meets certain requirements, working at least 20 hours per week. Your employer must be using the E-verify program in order for you to be employed.
How to apply for OPT

When you are ready to apply for OPT, you must request your DSO at your university to recommend the OPT. Your DSO will then make a recommendation by endorsing your I-20 form. You must also properly file Form I-765. It is in the Application for Employment Authorization with USCIS, and you must pay the required fee and prepare supplemental documents. When you are all done, mail your documents to USCIS.
What's next?
If you are an F-1 international student, remember to stay informed and do everything in a timely manner. The difference between OPT and CPT can be complicated, but it is an amazing opportunity for your career. CPT and OPT are both opportunities given to international students, so be sure to take them and make the best of your experience. Be patient and enjoy your work experience!
We hope that this difference between CPT vs. OPT helped you understand your future work options. If you have more questions about studying, living, or working abroad, make sure you check out some of our top blogs.
You can also email us any questions you can also contact us and let us know your thoughts in the comments below!
FAQs
Q1. How long is the OPT valid?
Answer – The OPT is valid for 12 months. However, it can be extended to 24 months.
Q2. How many hours can I work during a CPT?
Answer – You can work for a total of 40 hours per week during your CPT.
Q3. Can I work for more than CPT at a time?
Answer – Yes, you can work for more than CPT at a time. However, a separate CPT authorization is needed for each employer and each CPT segment.
Source: https://ischoolconnect.com/blog/difference-between-cpt-vs-opt/
Post a Comment for "Gap Between Cpt and Opt and Continue Employment"